The Importance and Artistry of Architectural Maquettes
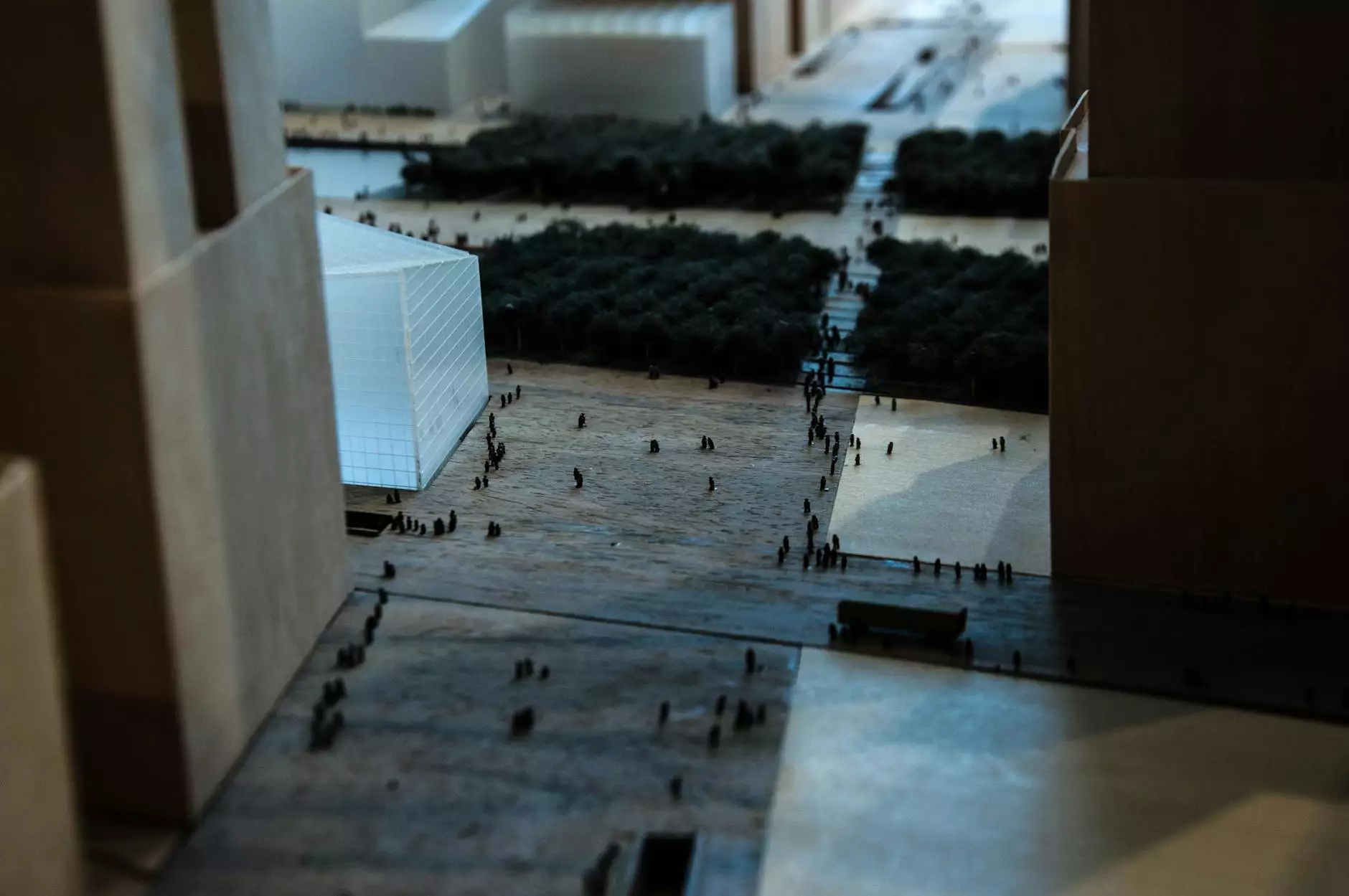

In the realm of architecture, the term architectural maquette embodies a blend of creativity, precision, and functionality. These miniature models serve as a crucial communication tool, allowing architects, designers, and clients to visualize concepts, evaluate spatial relationships, and understand the overall composition of structures before they become a reality. Let’s delve into the significance, process, and various types of architectural maquettes.
1. What is an Architectural Maquette?
An architectural maquette is a scale model representing a building or structure. Ranging from simple concepts to intricate designs, these models can be crafted from various materials, including paper, cardboard, wood, and plastic. They allow for tangible exploration of architectural ideas and help in conveying the architect's vision.
1.1 The History of Architectural Models
The practice of creating models dates back to ancient civilizations, where architects would use rudimentary forms to represent their designs. Throughout history, the complexity and sophistication of these maquettes have evolved, mirroring advancements in technology and changes in architectural styles.
2. Why Are Architectural Maquettes Important?
Architectural maquettes play a vital role in the architectural design process. They are not just artistic expressions but serve multiple important functions:
- Visual Communication: Maquettes provide a physical representation of ideas, allowing architects to communicate their concepts effectively to clients and stakeholders.
- Spatial Relationships: They help in understanding how different elements of a structure interact with each other and their environment.
- Design Iteration: Building maquettes allows for quick adjustments in design, enabling architects to experiment with different forms and functions.
- Client Engagement: An effective maquette can significantly enhance client interaction, making it easier for them to visualize the end product.
- Presentation: Maquettes are often used in presentations to exemplify the architect’s vision and approach.
2.1 Enhancing Creativity and Innovation
Creating an architectural maquette can be a profound creative exercise. As architects build physical models, their ideas take shape, prompting new thoughts and innovations. This hands-on process is crucial in transcending abstract ideas into tangible forms.
3. The Process of Creating Architectural Maquettes
Building an architectural maquette is a meticulous process that involves several stages:
3.1 Conceptualization
The first step involves brainstorming ideas and concepts that align with the project’s requirements and objectives. Architects may sketch designs and consider various materials and proportions during this phase.
3.2 Material Selection
Selecting the right materials is essential for the maquette's functionality and aesthetic appeal. Common materials used include:
- Cardboard: Inexpensive and easy to cut, ideal for preliminary models.
- Wood: Offers durability and a more refined finish.
- Foam Board: Lightweight and easy to manipulate.
- Plastics: Provide versatility and often used in final presentations.
3.3 Building the Maquette
Once materials are chosen, the next step is to assemble the model meticulously. This involves cutting, shaping, and joining materials to reflect the design effectively. Architects often use adhesives, pins, and other tools to ensure structural integrity.
3.4 Detailing and Finishing
To bring the architectural maquette to life, detailing is crucial. This can include adding texture, color, and landscaping elements to illustrate the environment surrounding the architectural design. Finishing touches can dramatically enhance the visual appeal and realism of the model.
4. Types of Architectural Maquettes
There are various types of architectural maquettes, each serving distinct purposes:
4.1 Conceptual Models
These are rough models used to explore initial ideas. They do not typically include intricate details but focus on proportion and spatial relationships.
4.2 Presentation Models
More refined, these models are designed for client presentations. They are detailed and often painted to represent final materials and finishes.
4.3 Working Models
These are functional models used to test systems and spatial interactions. They are often larger and may include moveable parts to demonstrate functionality.
4.4 Scale Models
Scale models represent an accurate size ratio of the actual building. These are often used in public presentations or exhibitions, providing a clear vision of the final outcome.
5. The Role of Technology in Architectural Maquettes
In recent years, technology has significantly influenced the creation and functionality of architectural maquettes:
5.1 3D Printing
This revolutionary technology allows architects to create highly accurate and complex models quickly. 3D printing has opened new avenues for experimentation and design sophistication.
5.2 Digital Models and Virtual Reality
Using software for digital modeling enhances precision. Architects can simulate how their structures will function within their environments, and virtual reality can provide immersive experiences of the designs.
6. The Future of Architectural Maquettes
The future of architectural maquettes looks promising as technology continues to evolve. Innovations in materials and digital fabrication techniques will enable architects to push the boundaries of design and functionality. Furthermore, as sustainability becomes paramount, the focus on eco-friendly materials for maquettes will likely increase.
As we move forward, the integration of augmented reality (AR) in architectural presentations can redefine how stakeholders interact with designs, providing an engaging experience that goes beyond traditional maquettes.
7. Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Architectural Maquettes
Architectural maquettes are not mere models; they are essential tools in the architectural process that help transform ideas into reality. They facilitate communication, foster creativity, and enrich the design experience for architects and clients alike. No matter how advanced technology becomes, the intrinsic value of a well-crafted architectural maquette will always hold a special place in the architectural community.
Explore More at Maquettes-Architecture.fr
If you are passionate about architectural maquettes and wish to learn more or possibly commission a project, visit maquettes-architecture.fr. Engage with us in exploring the artistry and importance of architectural modeling in today's world.